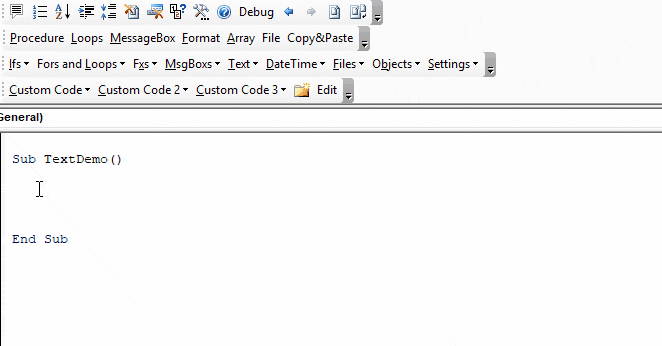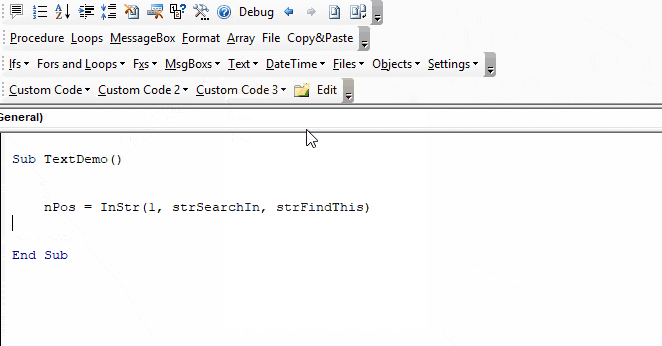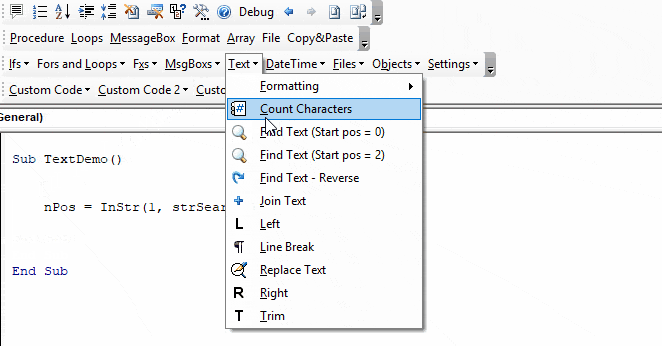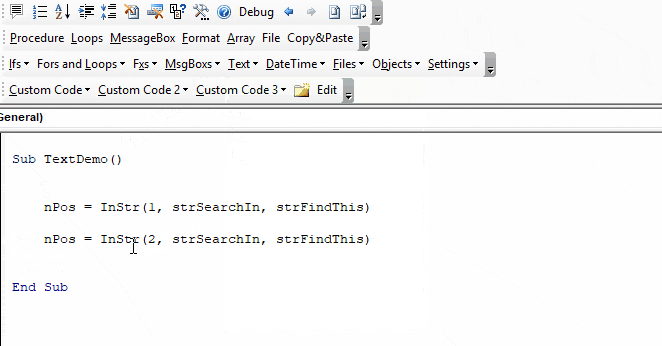
Определение первого вхождения одной строки в другую с помощью функции InStr из кода VBA Excel. Синтаксис функции, параметры, примеры использования.
InStr – это функция, которая предназначена для определения номера позиции первого вхождения одной строки в другую. Она возвращает значение типа Variant (Long).
Функция InStr ищет первое вхождение одной строки в другую с начала исходной строки. Для поиска первого совпадения с конца исходной строки используется функция InStrRev.
Функция InStr часто незаменима при определении параметров функций Left, Mid и Right. Также ее можно использовать для определения наличия искомой подстроки в заданной строке.
Еще есть в VBA Excel функция InStrB, которая работает с байтовыми данными, содержащимися в строке. Она возвращает позицию байта, а не символа первого вхождения одной строки в другую. Смотрите ниже Пример 3.
Синтаксис, параметры, значения
Синтаксис функции InStr
Полный вариант:
|
InStr([start], string1, string2, [compare]) |
Сокращенный вариант:
Чаще всего в VBA Excel используется сокращенный вариант функции со значениями необязательных параметров по умолчанию.
Параметры функции InStr
| Параметр | Описание | Значение по умолчанию |
|---|---|---|
| start | Необязательный аргумент.* Числовое выражение, которое задает начальную позицию для поиска. | 1 |
| string1 | Обязательный аргумент. Строковое выражение, в котором выполняется поиск. | – |
| string2 | Обязательный аргумент. Искомое строковое выражение. | – |
| compare | Необязательный аргумент. Задает тип сравнения строк. | –1** |
* Если задан аргумент compare, аргумент start является обязательным.
** Если аргумент compare не указан, используется значение инструкции Option Compare, заданное на уровне модуля. Если инструкция Option Compare в начале модуля отсутствует, используется ее значение по умолчанию – 0 (двоичное сравнение).
Если параметр start или параметр compare содержит значение NULL, возникает ошибка.
Значения аргумента «compare»
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Сравнение с помощью параметра инструкции Option Compare. |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | Двоичное (бинарное) сравнение.* |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | Текстовое сравнение.* |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | Сравнение на основе сведений из базы данных. Только для Microsoft Access. |
* При двоичном сравнении учитывается регистр букв, при текстовом – не учитывается.
Значения функции InStr
| Если | Возвращаемое значение |
|---|---|
| string2 найдена в string1 | Позиция первого найденного соответствия. |
| string2 не найдена в string1 | 0 |
| string2 является пустой | start |
| string2 равна Null | Null |
| string1 является пустой | 0 |
| string1 равна Null | Null |
| start больше длины string1 | 0 |
Примеры использования в VBA Excel
Пример 1
Самый простой пример:
|
Sub Test1() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «Фернандо») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 9 End Sub |
Пример 2
В этом примере, используя одинаковые строки, в которых выполняется поиск, и искомые подстроки, применим разные виды сравнения – двоичное (бинарное) и текстовое, и посмотрим на результаты.
|
Sub Test2() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 0) MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 36 (поиск с учетом регистра символов) x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 1) MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 18 (поиск без учета регистра символов) End Sub |
Обратите внимание: несмотря на то, что начало поиска мы задали с 10 символа, номер позиции первого вхождения считается с начала строки, в которой выполняется поиск.
Пример 3
В этом примере посмотрим на результаты посимвольного и побайтового сравнения, опять же используя одинаковые строки и искомые подстроки.
|
Sub Test3() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 4 x = InStrB(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 7 End Sub |
Результат 7 при побайтовом сравнении получен для кодировки, у которой один символ составляет 2 байта.
In this Article
- INSTR Function
- Instr Example
- Instr Syntax
- Instr Start Position
- Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
- InstrRev Function
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- InString Examples
- If String Contains Substring
- Find Text String in a Cell
- Find Position of a Character in a String
- Search String for Word
- If Variable Contains String
- Instr and the Left Function
- Using Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
INSTR Function
The VBA Instr Function checks if a string of text is found in another string of text. It returns 0 if the text is not found. Otherwise it returns the character position where the text is found.
The Instr Function performs exact matches. The VBA Like Operator can be used instead to perform inexact matches / pattern matching by using Wildcards.
Instr Example
The following code snippet searches the string “Look in this string” for the word “Look”. The Instr Function returns 1 because the text is found in the first position.
Sub FindSomeText()
MsgBox InStr("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubThis second example returns 7 because the text is found starting in the 7th position:
Sub FindSomeText2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "Look")
End SubImportant! The Instr Function is case-sensitive by default. This means “look” will not match with “Look”. To make the test case-insensitive read below.
Instr Syntax
The syntax for the Instr function is as follows:
Instr( [start], string, substring, [compare] )[start] (optional) – This optional argument is the starting position of the search. Enter 1 to start searching from position 1 (or leave blank). Enter 5 to start searching from position 5. Important! The INSTR function calculates the character position by counting from 1 NOT from the [start] position.
string – The string of text to search in.
substring – The string of text to find in the primary string.
[compare] (optional) – By default, Instr is case-sensitive. By setting this argument you can make Instr Case insensitive:
|
Argument vb Value |
Argument Integer | Description |
| vbBinaryCompare |
0 |
(Default) Case-sensitive |
|
vbTextCompare |
1 |
Not Case-sensitive |
|
vbDatabaseCompare |
2 |
MS Access Only. Uses information in the database to perform comparison. |
Instr Start Position
The Instr start position allows you to indicate the character position where you will begin your search. Keep in mind however, the Instr output will always count from 1.
Here we set the start position to 3 to skip the first B:
Sub Instr_StartPosition()
MsgBox InStr(3, "ABC ABC", "B")
End SubThe result is 6 because the second B is the 6th character in the string.
Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
By default, VBA treats “L” different from “l”. In other words, VBA is case-sensitive. This is true of all text functions. To make VBA case-insensitive, set the [compare] argument to 1 or vbTextCompare.
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase()
MsgBox InStr(1, "Don't Look in this string", "look", vbTextCompare)
End SubAlternatively, you can add Option Compare Text to the top of your code module:
Option Compare TextOption Compare Text
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "look")
End SubOption Compare Text will impact all of the code in that module. I personally place this at the top of any module that deals with text because I never care about case differences.
InstrRev Function
The Instr Function searches from the left. Instead you can search from the right using the InstrRev Function. The InstrRev Function works very similarly to the Instr function.
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubJust like the Instr function this will return 1 because there is only one instance of “Look” in the text. But if we add a second “Look”, you’ll see that it returns the position of the right-most “Look”:
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string Look", "Look")
End SubNext we will review more Instr examples.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
InString Examples
If String Contains Substring
Here we will use an If statement to test if a string contains a a substring of text:
Public Sub FindSomeText()
If InStr("Look in this string", "look") = 0 Then
MsgBox "No match"
Else
MsgBox "At least one match"
End If
End SubFind Text String in a Cell
You can also find a string in a cell:
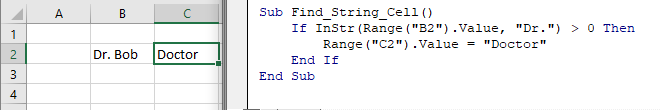
Sub Find_String_Cell()
If InStr(Range("B2").Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
Range("C2").Value = "Doctor"
End If
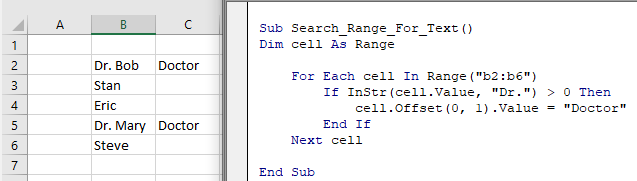
End SubOr loop through a range of cells to test if the cells contain some text:
Sub Search_Range_For_Text()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b6")
If InStr(cell.Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Doctor"
End If
Next cell
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Find Position of a Character in a String
This code will find the position of a single character in a string and assign the position to a variable:
Sub Find_Char()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "L")
End SubSearch String for Word
This code will search a string for a word:
Sub Search_String_For_Word()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "Look")
If n = 0 Then
MsgBox "Word not found"
Else
MsgBox "Word found in position: " & n
End If
End SubIf Variable Contains String
This code will test if a string variable contains a string of text:
Sub Variable_Contains_String()
Dim str As String
str = "Look Here"
If InStr(str, "Here") > 0 Then
MsgBox "Here found!"
End If
End SubInstr and the Left Function
Instr can be used along with other text functions like Left, Right, Len, and Mid to trim text.
With the Left function you can output the text prior to a string of text:
Sub Instr_Left()
Dim str As String
Dim n As Long
str = "Look Here"
n = InStr(str, "Here")
MsgBox Left(str, n - 1)
End SubUsing Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
To learn more, read our article: VBA text functions
<<Return to VBA Examples
Just to complete the possibilities listed, I would like to demonstrate how you can use Split() for an all-round function with the following variants depending on the optional argument n passed:
- a) show whether a substring was found at all (-1 or omitted as default value)
- b) show how many substrings were found (0) ,
- c) show at which position the nth substring was found (1 .. n).
Function StrIncludes( _
ByVal s As String, _
Optional ByVal IncludeString As String = ",", _
Optional n As Long = -1 _
) As Long
'Purp.: find specified substring based on numeric value n
'Note : 2nd argument IncludeString is optional (default value is comma if omitted)
' 3rd argument n: -1~~>only boolean; 0~~>count(s); 1..n ~~>position
Dim tmp: tmp = Split(s, IncludeString)
StrIncludes = UBound(tmp) > 0 ' a) boolean return value indicating a found substring
Select Case n ' individual numeric values:
Case 0 ' b) return Count(s), not boolean value
StrIncludes = UBound(tmp)
Case 1
StrIncludes = IIf(StrIncludes, Len(tmp(n - 1)) + n, 0)
Case Is > 1 ' c) return Position of nth finding
If n > UBound(tmp) Then StrIncludes = 0: Exit Function
StrIncludes = IIf(StrIncludes, Len(tmp(0)) + n, 0)
Dim i As Long
For i = 2 To n: StrIncludes = StrIncludes + Len(tmp(i - 1)): Next
End Select
End Function
Example call
Sub ExampleCall()
' define base string
Dim s As String
s = "Take this example string, does it contain a comma, doesn't it?"
'a) check if base string contains indicated search string, e.g. a comma (default value)
Debug.Print "Is Found: " & CBool(StrIncludes(s)) ' ~~> Is Found: True
'b) get number of substrings
Debug.Print "Count(s): " & StrIncludes(s, , 0) ' ~~> Count(s): 2
'c) get position of nth substring
Debug.Print "~~~ Findings of nth substring ~~~ "
Dim n As Long
For n = 1 To 3
Debug.Print n & ordinalSuffix(n) & " substring at Pos.: " & StrIncludes(s, , n)
Next
End Sub
Function ordinalSuffix(ByVal number As Long) As String
Dim suffixes: suffixes = Split(" st nd rd th")
ordinalSuffix = suffixes(Abs(number))
End Function
Debugging results in immediate window
Is Found: Wahr
Count(s): 2
~~~ Findings of nth substring ~~~
1st substring at Pos.: 25
2nd substring at Pos.: 50
3rd substring at Pos.: 0 ' no finding at all
В этой статье разберем работу со строками в VBA на примерах функций InStr, LCASE, UCase, Left, Right, Mid, LTrim, RTrim, Trim, Len, Replace, Space, StrComp, String, StrReverse.
Строки — это последовательность символов, которая может состоять либо из алфавитов, цифр, специальных символов, либо из всех них. Переменная называется строкой, если она заключена в двойные кавычки «».
Содержание:
- Синтаксис
- Примеры
- Строковые функции
- Название функции и описание
- InStr
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- LCASE
- Синтаксис
- пример
- UCase
- Синтаксис
- пример
- Left
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- Right
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- Mid
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- LTrim
- Синтаксис
- пример
- RTrim
- Синтаксис
- пример
- Trim
- Синтаксис
- пример
- Len
- Синтаксис
- пример
- Replace
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- Space
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- StrComp
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- String
- Синтаксис
- Параметр Описание
- пример
- StrReverse
- Синтаксис
- пример
Синтаксис
variablename = "string"
Примеры
str1 = "string" ' Only Alphabets str2 = "132.45" ' Only Numbers str3 = "!@#$;*" ' Only Special Characters Str4 = "Asc23@#" ' Has all the above
Строковые функции
Существуют предопределенные функции VBA String, которые помогают разработчикам эффективно работать со строками. Ниже приведены методы String, поддерживаемые в VBA. Пожалуйста, нажмите на каждый из методов, чтобы знать подробно.
Название функции и описание
Функция InStr возвращает первое вхождение одной строки в другую строку. Поиск происходит слева направо.
Синтаксис
InStr([start,]string1,string2[,compare])
Параметр Описание
- Пуск — необязательный параметр. Указывает начальную позицию для поиска. Поиск начинается с первой позиции слева направо.
- String1 — требуемый параметр. Строка для поиска.
- String2 — требуемый параметр. Строка, по которой выполняется поиск String1.
- Compare — Необязательный параметр. Указывает сравнение строк.Он может принимать следующие значения.
- 0 = vbBinaryCompare — выполняет двоичное сравнение (по умолчанию)
- 1 = vbTextCompare — выполняет сравнение текста
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim Var As Variant
Var = "Microsoft VBScript"
MsgBox ("Line 1 : " & InStr(1, Var, "s"))
MsgBox ("Line 2 : " & InStr(7, Var, "s"))
MsgBox ("Line 3 : " & InStr(1, Var, "f", 1))
MsgBox ("Line 4 : " & InStr(1, Var, "t", 0))
MsgBox ("Line 5 : " & InStr(1, Var, "i"))
MsgBox ("Line 6 : " & InStr(7, Var, "i"))
MsgBox ("Line 7 : " & InStr(Var, "VB"))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : 6
Line 2 : 0
Line 3 : 8
Line 4 : 9
Line 5 : 2
Line 6 : 16
Line 7 : 11
Возвращает первое вхождение указанной подстроки. Поиск происходит слева направо.
InStrRev
Функция InStrRev возвращает первое вхождение одной строки в другую строку. Поиск происходит справа налево.
Синтаксис
InStrRev(string1,string2[,start,[compare]])
Параметр Описание
- String1 — требуемый параметр. Строка для поиска.
- String2 — требуемый параметр. Строка, по которой выполняется поиск String1.
- Пуск — необязательный параметр. Указывает начальную позицию для поиска. Поиск начинается с первой позиции справа налево.
- Compare — Необязательный параметр. Указывает сравнение строк.Он может принимать следующие значения.
- 0 = vbBinaryCompare — выполняет двоичное сравнение (по умолчанию)
- 1 = vbTextCompare — выполняет сравнение текста
пример
Добавьте кнопку и установите следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & InStrRev(var,"s",10))
msgbox("Line 2 : " & InStrRev(var,"s",7))
msgbox("Line 3 : " & InStrRev(var,"f",-1,1))
msgbox("Line 4 : " & InStrRev(var,"t",5))
msgbox("Line 5 : " & InStrRev(var,"i",7))
msgbox("Line 6 : " & InStrRev(var,"i",7))
msgbox("Line 7 : " & InStrRev(var,"VB",1))
End Sub
После выполнения вышеуказанного скрипта он производит следующий результат.
Line 1 : 6
Line 2 : 6
Line 3 : 8
Line 4 : 0
Line 5 : 2
Line 6 : 2
Line 7 : 0
Возвращает первое вхождение указанной подстроки. Поиск происходит справа налево.
LCASE
Функция LCase возвращает строку после преобразования введенной строки в строчные буквы.
Синтаксис
Lcase(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и поместите следующую функцию внутри нее.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & LCase(var))
var = "MS VBSCRIPT"
msgbox("Line 2 : " & LCase(var))
var = "microsoft"
msgbox("Line 3 : " & LCase(var))
End Sub
После выполнения вышеуказанного скрипта он производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : microsoft vbscript
Line 2 : ms vbscript
Line 3 : microsoft
Возвращает нижний регистр указанной строки.
UCase
Функция UCase возвращает строку после преобразования введенной строки в буквы буквы UPPER.
Синтаксис
UCase(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и поместите следующую функцию внутри нее.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & UCase(var))
var = "MS VBSCRIPT"
msgbox("Line 2 : " & UCase(var))
var = "microsoft"
msgbox("Line 3 : " & UCase(var))
End Sub
После выполнения вышеуказанного скрипта он производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : MICROSOFT VBSCRIPT
Line 2 : MS VBSCRIPT
Line 3 : MICROSOFT
Возвращает верхний регистр указанной строки.
Left
Функция Left возвращает указанное количество символов с левой стороны данной входной строки.
Синтаксис
Left(String, Length)
Параметр Описание
- String — обязательный параметр. Строка ввода, из которой указанное число символов должно быть возвращено с левой стороны.
- Длина — требуемый параметр. Целое число, определяющее количество возвращаемых символов.
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var as Variant
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & Left(var,2))
var = "MS VBSCRIPT"
msgbox("Line 2 : " & Left(var,5))
var = "microsoft"
msgbox("Line 3 : " & Left(var,9))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : Mi
Line 2 : MS VB
Line 3 : microsoft
Возвращает определенное количество символов с левой стороны строки.
Right
Функция Right возвращает указанное количество символов с правой стороны данной входной строки.
Синтаксис
Right(String, Length)
Параметр Описание
- String — обязательный параметр. Строка ввода, из которой указанное число символов должно быть возвращено с правой стороны.
- Длина — требуемый параметр. Целое число, которое задает количество возвращаемых символов.
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & Right(var,2))
var = "MS VBSCRIPT"
msgbox("Line 2 : " & Right(var,5))
var = "microsoft"
msgbox("Line 3 : " & Right(var,9))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : pt
Line 2 : CRIPT
Line 3 : microsoft
Возвращает определенное количество символов с правой стороны строки.
Mid
Mid функция возвращает указанное количество символов из заданной входной строки.
Синтаксис
Mid(String,start[,Length])
Параметр Описание
- String — обязательный параметр. Строка ввода, из которой задано количество символов, которые нужно вернуть.
- Начало — требуемый параметр. Целое число, определяющее начальную позицию строки.
- Длина — необязательный параметр. Целое число, определяющее количество возвращаемых символов.
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var as Variant
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Line 1 : " & Mid(var,2))
msgbox("Line 2 : " & Mid(var,2,5))
msgbox("Line 3 : " & Mid(var,5,7))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : icrosoft VBScript
Line 2 : icros
Line 3 : osoft V
Возвращает определенное количество символов из строки на основе указанных параметров.
LTrim
Функция Ltrim удаляет пробелы с левой стороны строки.
Синтаксис
LTrim(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click() Dim var as Variant var = " Microsoft VBScript" msgbox "After Ltrim : " & LTrim(var) End Sub
Когда вы выполняете функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
After Ltrim : Microsoft VBScript
Возвращает строку после удаления пробелов в левой части указанной строки.
RTrim
Функция Rtrim удаляет пробелы с правой стороны строки.
Синтаксис
RTrim(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var as Variant
var = "Microsoft VBScript "
msgbox("After Rtrim : " & RTrim(var))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
After Rtrim : Microsoft VBScript
Возвращает строку после удаления пробелов в правой части указанной строки.
Trim
Функция Trim удаляет как ведущее, так и конечное пустое пространство данной входной строки.
Синтаксис
Trim(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
var = "Microsoft VBScript"
var = " Microsoft VBScript "
msgbox ("After Trim : " & Trim(var))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
After trim : Microsoft VBScript
Возвращает строковое значение после удаления как верхнего, так и конечного пробелов.
Len
Функция Len возвращает длину данной входной строки, включая пробелы.
Синтаксис
Len(String)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var1 as Variant
Dim var2 as Variant
var1 ="Microsoft VBScript"
msgbox("Length of var1 is : " & Len(var1))
var2 = " Microsoft VBScript "
msgbox ("Length of var2 is : " & Len(var2))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Length of var1 is : 18
Length of var2 is : 36
Возвращает длину данной строки.
Replace
Функция Replace заменяет указанную часть строки на определенную строку, указанное количество раз.
Синтаксис
Replace(string,find,replacewith[,start[,count[,compare]]])
Параметр Описание
- String — обязательный параметр. Строка ввода, которую нужно искать для замены.
- Find — требуемый параметр. Часть строки, которая будет заменена.
- Replacewith — обязательный параметр. Строка замены, которая будет заменена на параметр find.
- Start — необязательный параметр. Задает начальную позицию, из которой нужно искать и заменять строку. Значение по умолчанию — 1.
- Count — необязательный параметр. Указывает количество раз, которое должна выполняться замена.
- Compare — Необязательный параметр. Указывает метод сравнения, который будет использоваться. Значение по умолчанию — 0.
- 0 = vbBinaryCompare — выполняет двоичное сравнение
- 1 = vbTextCompare — выполняет текстовое сравнение
пример
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var as Variant
var = "This is VBScript Programming"
'VBScript to be replaced by MS VBScript
msgbox("Line 1: " & Replace(var,"VBScript","MS VBScript"))
'VB to be replaced by vb
msgbox("Line 2: " & Replace(var,"VB","vb"))
''is' replaced by ##
msgbox("Line 3: " & Replace(var,"is","##"))
''is' replaced by ## ignores the characters before the first occurence
msgbox("Line 4: " & Replace(var,"is","##",5))
''s' is replaced by ## for the next 2 occurences.
msgbox("Line 5: " & Replace(var,"s","##",1,2))
''r' is replaced by ## for all occurences textual comparison.
msgbox("Line 6: " & Replace(var,"r","##",1,-1,1))
''t' is replaced by ## for all occurences Binary comparison
msgbox("Line 7: " & Replace(var,"t","##",1,-1,0))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1: This is MS VBScript Programming
Line 2: This is vbScript Programming
Line 3: Th## ## VBScript Programming
Line 4: ## VBScript Programming
Line 5: Thi## i## VBScript Programming
Line 6: This is VBSc##ipt P##og##amming
Line 7: This is VBScrip## Programming
Возвращает строку после замены строки другой строкой.
Space
Функция Space заполняет строку конкретным количеством пробелов.
Синтаксис
space(number)
Параметр Описание
Номер — требуемый параметр. Количество пробелов, которые мы хотим добавить к данной строке.
пример
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click() Dim var1 as Variant var1 = "Microsoft" Dim var2 as Variant var2 = "VBScript" msgbox(var1 & Space(2)& var2) End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Microsoft VBScript
Заполняет строку указанным количеством пробелов.
StrComp
Функция StrComp возвращает целочисленное значение после сравнения двух заданных строк. Он может возвращать любое из трех значений -1, 0 или 1 на основе входных строк для сравнения.
- Если String1 меньше String2, то StrComp возвращает -1
- Если String1 равно String2, то StrComp возвращает 0
- Если String1 больше String2, то StrComp возвращает 1
Синтаксис
StrComp(string1,string2[,compare])
Параметр Описание
- String1 — требуемый параметр. Первое строковое выражение.
- String2 — требуемый параметр. Второе строковое выражение.
- Compare — Необязательный параметр. Указывает сравнение строк.Он может принимать следующие значения.
- 0 = vbBinaryCompare — выполняет двоичное сравнение (по умолчанию)
- 1 = vbTextCompare — выполняет сравнение текста
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
Dim var1 as Variant
msgbox("Line 1 :" & StrComp("Microsoft","Microsoft"))
msgbox("Line 2 :" &StrComp("Microsoft","MICROSOFT"))
msgbox("Line 3 :" &StrComp("Microsoft","MiCrOsOfT"))
msgbox("Line 4 :" &StrComp("Microsoft","MiCrOsOfT",1))
msgbox("Line 5 :" &StrComp("Microsoft","MiCrOsOfT",0))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 :0
Line 2 :1
Line 3 :1
Line 4 :0
Line 5 :1
Возвращает целочисленное значение после сравнения двух указанных строк.
String
Функция String заполняет строку указанным символом для указанного количества раз.
Синтаксис
String(number,character)
Параметр Описание
- Номер — требуемый параметр. Целочисленное значение, которое будет повторяться в течение определенного количества раз против параметра символа.
- Символ — требуемый параметр. Значение символа, которое должно повторяться определенное количество раз.
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
msgbox("Line 1 :" & String(3,"$"))
msgbox("Line 2 :" & String(4,"*"))
msgbox("Line 3 :" & String(5,100))
msgbox("Line 4 :" & String(6,"ABCDE"))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 :$$$
Line 2 :****
Line 3 :ddddd
Line 4 :AAAAAA
Возвращает строку с указанным символом для указанного количества раз.
StrReverse
Функция StrReverse меняет указанную строку.
Синтаксис
StrReverse(string)
пример
Добавьте кнопку и добавьте следующую функцию.
Private Sub Constant_demo_Click()
msgbox("Line 1 : " & StrReverse("VBSCRIPT"))
msgbox("Line 2 : " & StrReverse("My First VBScript"))
msgbox("Line 3 : " & StrReverse("123.45"))
End Sub
Когда вы выполняете вышеуказанную функцию, она производит следующий вывод.
Line 1 : TPIRCSBV
Line 2 : tpircSBV tsriF yM
Line 3 : 54.321
Возвращает строку после изменения последовательности символов данной строки.
С уважением, авторы сайта Компьютерапия
Понравилась статья? Поделитесь ею с друзьями и напишите отзыв в комментариях!
VBA InStr function in Excel is categorized as a Text/String function in VBA. It is a built-in function in MS Office Excel. Finds the position of specified sub-string with the given string. Returns the first occurrence position as a integer value. If it doesn’t find specified sub string, It returns a value ‘0’. Performs a case sensitive search. It has four parameters.
The VBA InStr function use in either procedure or function in a VBA editor window in Excel. We can use this VBA InStr function any number of times in any number of procedures or functions. In the following section we learn what is the syntax and parameters of the InStr function, where we can use this VBA InStr function and real-time examples.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Syntax of VBA InStr Function in Excel:
- Parameters or Arguments:
- Where we can apply or use the InStr Function?
- Example 1: Search specified substring in given string, starting at position 1
- Example 2: Search specified substring within string, starting at position 3
- Example 3: InStr Function using ‘vbBinaryCompare’ (Case Sensitive Search)
- Example 4: InStr Function using vbTextCompare (Avoid Case Sensitive Search)
- Example 5: Search for ‘@’ symbol in specified email
- Example 6: Search for ‘.’ and file extension within specified file name
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
The syntax of the VBA InStr function is
InStr ([start], string, substring, [compare])
In the above syntax the second and third arguments are mandatory (string & substring) parameters. And the first and last two parameters are optional (start & compare) Arguments.
Parameters or Arguments:
Where
Start: The start is an optional argument, and its default value is ‘1’. It represents the starting position for the search. It accepts integer type input value. If we don’t specify any value, default it considers default value as one.
String: The string is a mandatory argument. The string in which we want to search.
Substring: The substring is a mandatory argument. The substring that you want to find within string.
Compare: The compare is an optional argument. It represents which type of comparison needs to perform. It has four numeric values. It we don’t specify any value, default it considers a binary comparison. Here are the different four comparisons, which are shown in the below table.
| VBA Compare | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Performs a comparision using the ‘option compare’ |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | Performs a Binary comparison |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | Performs a Textual comparison |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | Microsoft Access only. Performs a comparison based on information in your database. |
Where we can apply or use the VBA InStr Function in Excel?
We can use this VBA InStr function in MS Office 365, MS Excel 2016, MS Excel 2013, 2011, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel 2016 for Mac, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel Online, Excel for iPhone, Excel for iPad, Excel for Android tablets and Excel for Android Mobiles.
Example 1: Search specified substring in given string, starting at position 1
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 1
'Search for "if" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex1()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'if' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "if")
'or
iPosition = InStr(sWord, "if")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F8") = "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'if' position: " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
In the above example ‘iPosition & sWord’ are declared as an integer and string data type. This variable ‘iPosition’ now contains the starting position of substring.
Output: Here is the screen shot of first example output.
Example 2: Search specified substring within string, starting at position 3
Here is another example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 3
'Search for "if" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 3.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex2()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'if' in given string
iPosition = InStr(3, sWord, "if")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F11") = "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of second example output.
Example 3: InStr Function using ‘vbBinaryCompare’ (Case Sensitive Search)
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds ‘b’ substring in within given string, starting at position 1. Where ‘b’ is a small letter. It returns ‘0’ as an output. Notice fourth argument in InStr function. It performs a binary comparison.
'Search for "b" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex3()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'b' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "b")
‘or
‘iPosition =InStr(1, sWord, "b", vbBinaryCompare)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F14") = "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Note: VBA InStr is a Case sensitive search.
Output: Here is the screen shot of third example output.
Example 4: InStr Function using vbTextCompare (Avoid Case Sensitive Search)
Here is one more example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds ‘b’ substring in within given string, starting at position 1. Where ‘b’ is a small letter, but It avoids case sensitive search and returns ‘9’ as an output. Notice fourth argument in InStr function. It performs a textual comparison.
'Search for "b" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex4()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'b' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "b", vbTextCompare)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F17") = "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of fourth example output.
Example 5: Search for ‘@’ symbol in specified email
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 1. We can also search special characters within string. Sometimes we want to search ‘@’ position in email. Let’s see.
'Search for "@" in string "abcde@gmail.com", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex5()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "abcde@gmail.com"
'Searh for '@' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "@")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("I8") = "The Special Character '@' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The Special Character '@' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of fifth example output.
Example 6: Search for ‘.’ and file extension within specified file name
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring(.) in within given string, starting at position 1. Most of the time while writing VBA codes we try to extract file extension or file name. Before that we need to identify ‘.’ Position In file name.
'Search for '.' and file extension in the file name "xyz.xlsm"
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex6()
'Variable declarations
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
Dim sFileExtn As String
sWord = "xyz.xlsm"
'Search file extension in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, ".")
'Get File Extension
sFileExtn = Right(sWord, Len(sWord) - iPosition)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("I11") = "Specified File Extension is : " & sFileExtn
'Display output message
MsgBox "Specified File Extension is : " & sFileExtn, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of sixth example output.
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays in Excel Blog
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers